Research Datasets
Own Collected Research Datasets

ArASL: Arabic Alphabets Sign Language Dataset
A fully-labelled dataset of Arabic Sign Language (ArSL) images is developed for research related to sign language recognition. The dataset will provide researcher the opportunity to investigate and develop automated systems for the deaf and hard of hearing people using machine learning, computer vision and deep learning algorithms. The contribution is a large fully-labelled dataset for Arabic Sign Language (ArSL) which is made publically available and free for all researchers. The dataset which is named ArSL2018 consists of 54,049 images for the 32 Arabic sign language sign and alphabets collected from 40 participants in different age groups. Different dimensions and different variations were present in images which can be cleared using pre-processing techniques to remove noise, center the image, etc.
The dataset is made available publicly at: https://data.mendeley.com/datasets/y7pckrw6z2/1
Citation:Latif, Ghazanfar, Nazeeruddin Mohammad, Jaafar Alghazo, Roaa AlKhalaf, and Rawan AlKhalaf. “ArASL: Arabic alphabets sign language dataset.” Data in brief 23 (2019): 103777.

ArTS: Arabic Traffic Sign Dataset
A new dataset for Arabic Traffic Signs is developed for the selected most common 24 Arabic traffic signs. The dataset consists of 2,718 real captured images and 57,078 augmented images for 24 Arabic traffic signs. The images are captured from three connected cities (Khobar, Dammam and Dhahran) in the Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia. The newly developed dataset consisting of 2,718 real images is randomly partitioned into 80% percent training set (2,200 images) and 20% percent testing set (518) images. Augmented dataset of 57,078 images with 10,878 images for testing and 46,200 images for testing. Due to large file size, the Augmented training dataset is uploaded as two compressed files.
The dataset is made available publicly at: https://data.mendeley.com/datasets/4tznkn45mx/1
Citation: Latif, Ghazanfar; Alghazo, Jaafar; Alghmgham, Danyah A.; Alzubaidi, Loay (2020), “ArTS: Arabic Traffic Sign Dataset”, Mendeley Data, V1, doi: 10.17632/4tznkn45mx.1
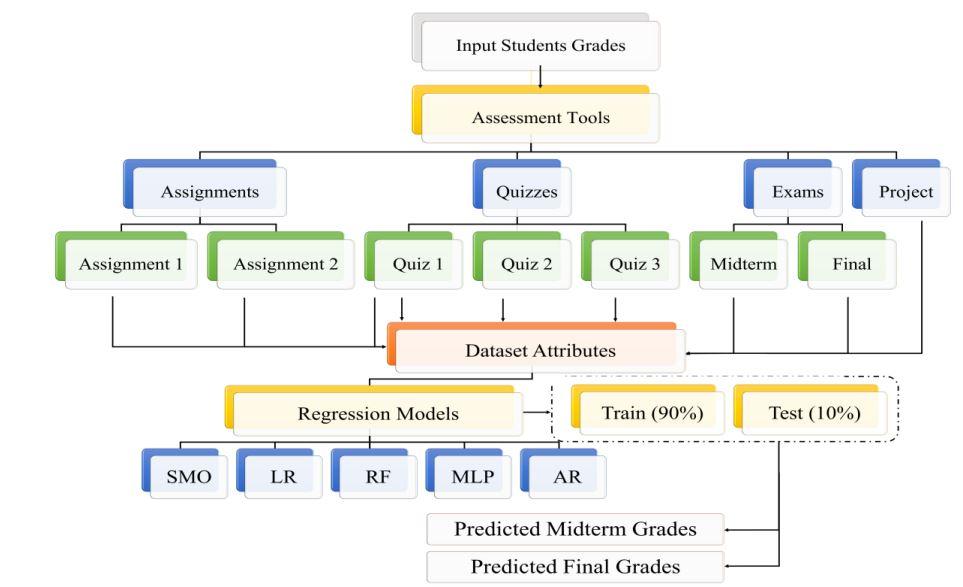
Students’ Grades Dataset for Identifying students “at Risk”
A dataset was developed including students’ grades in various courses from a private university in Saudi Arabia. The dataset comprised 250 students. Courses with the same assessment tools and grading schemes were chosen to standardize the grading scheme for each assessment item. To this end, undergraduate courses from the College of Computer Engineering and Science were included. The dataset covered a period of three semesters with different students each semester. The dataset described the max grade for each assessment tool (Assignment 1, Assignment 2, Quiz 1, etc.).
Please contact to get the dataset: glatif@pmu.edu.sa
Citation: Latif, G., Alghazo, R., Pilotti, M. A., & Brahim, G. B. (2021). Identifying” At-Risk” Students: An AI-based Prediction Approach. International Journal of Computing and Digital System.
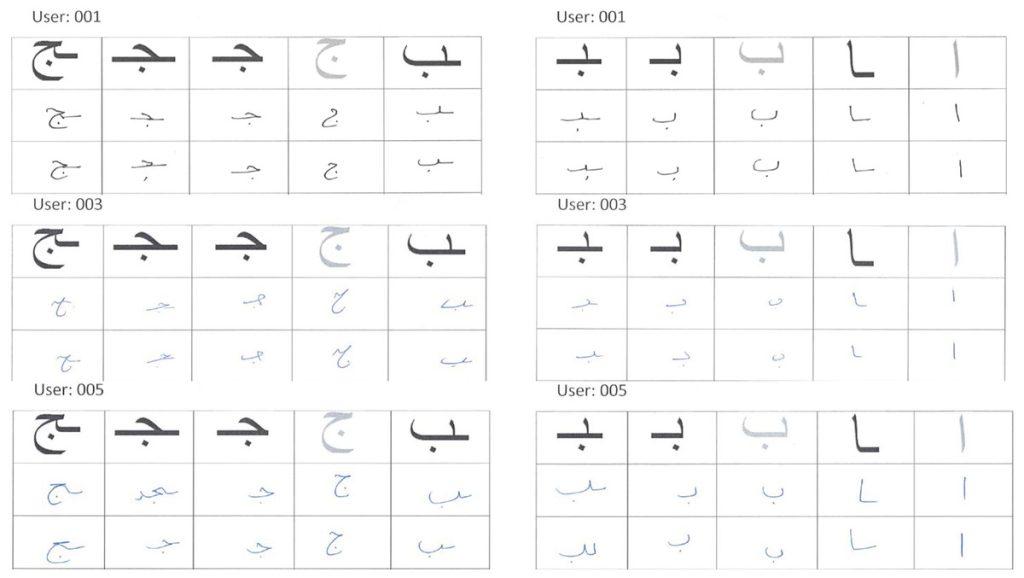
Writer Verification of partially Damaged Handwritten Arabic Documents Dataset
The extracted characters dataset consisted of characters cropped from user handwritten Arabic text. The users were asked to write Arabic text (consisting of ten Arabic words). The set of words were selected such that they covered the entire set of Arabic alphabet characters (but not all character shape variations). The characters were extracted from these words manually. The complete dataset consists of 10, 780 extracted characters from different users.
Article and dataset: https://peerj.com/articles/cs-955/
Citation: 2022. Writer verification of partially damaged handwritten Arabic documents based on individual character shapes. PeerJ Computer Science 8:e955 https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj-cs.955
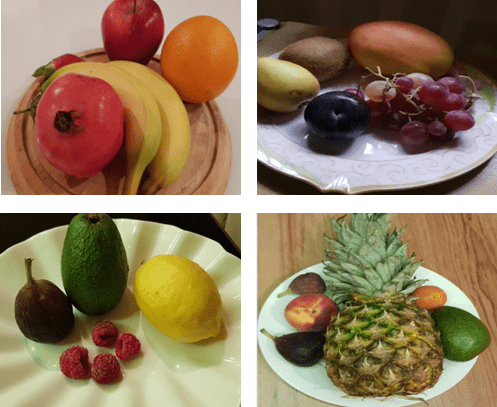
Fruit Images for Fruit Detection and Automatic Calories Estimation
A dataset of fully labelled images of 20 diverse kinds of fruits and 20 kinds of vegetables is developed for research purposes in the area of detection, recognition, classification and segmentation of fruits and vegetables for calories estimation. The dataset consists of 41,509 images for 16 different classes; 8 classes of fruits and 8 classes of vegetables.
Please contact to get the dataset: glatif@pmu.edu.sa
Citation: Latif, G., Alsalem, B., Mubarky, W., Mohammad, N., & Alghazo, J. (2020, April). Automatic Fruits Calories Estimation through Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 6th International Conference on Computer and Technology Applications (pp. 17-21).
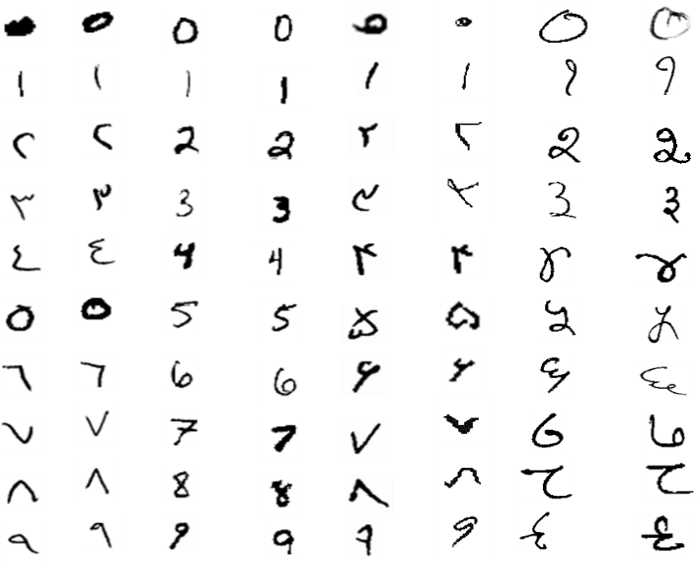
Arabic Handwritten Numerals Dataset
Please contact to get the dataset: glatif@pmu.edu.sa
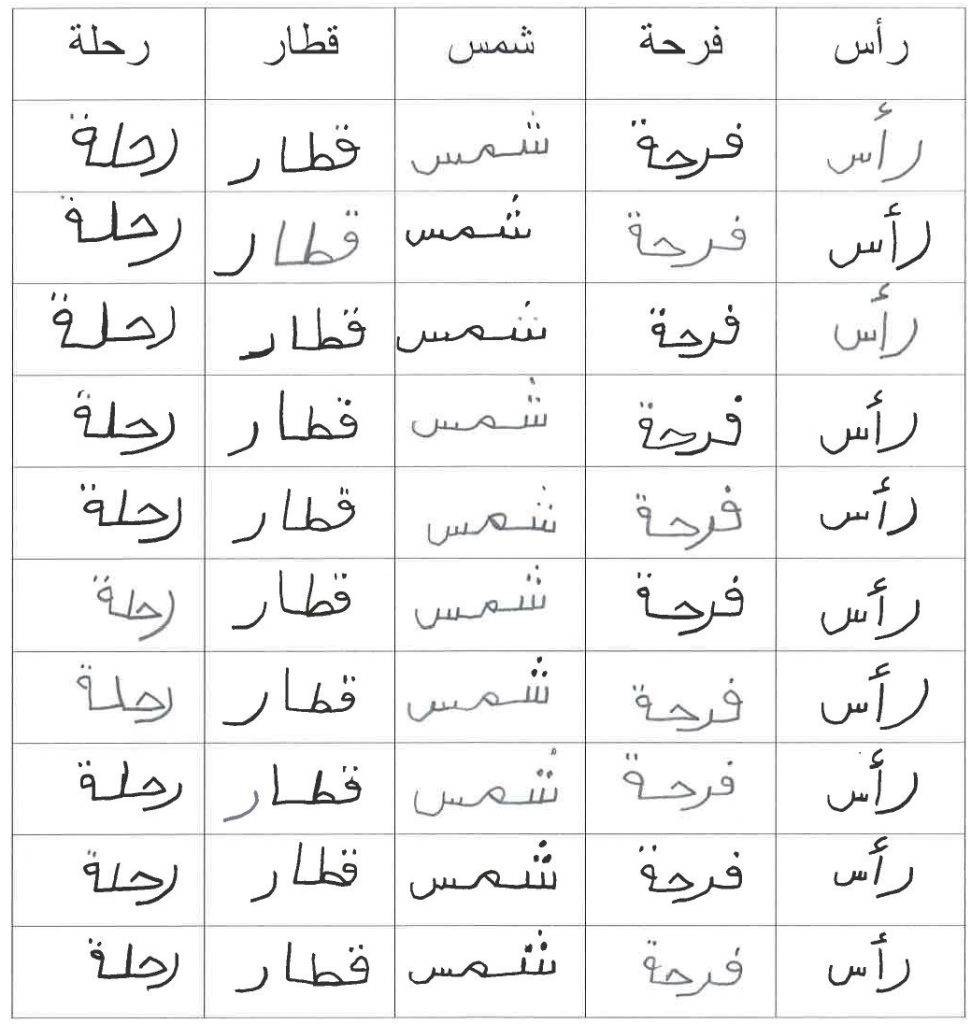
Arabic Handwritten Words Dataset
Please contact to get the dataset: glatif@pmu.edu.sa
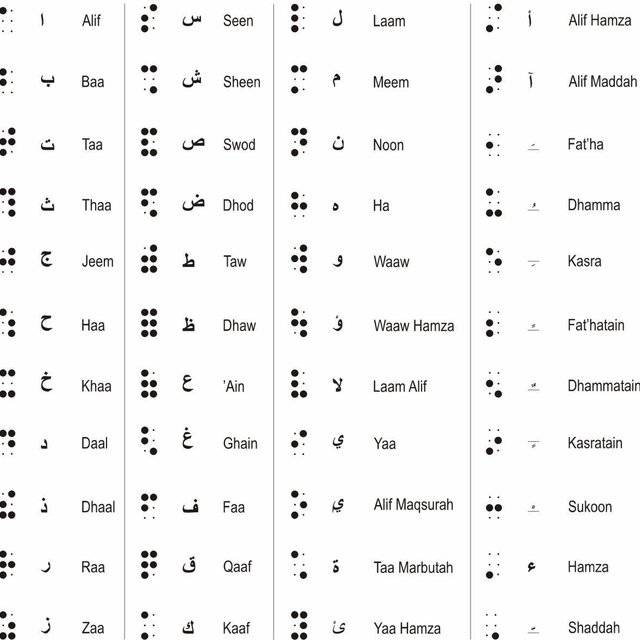
Arabic Braille Language Dataset
Please contact to get the dataset: glatif@pmu.edu.sa

Arabic Hate Speech Dataset
Please contact to get the dataset: glatif@pmu.edu.sa
Microscopic Minerals Grains Dataset
Please contact to get the dataset: glatif@pmu.edu.sa
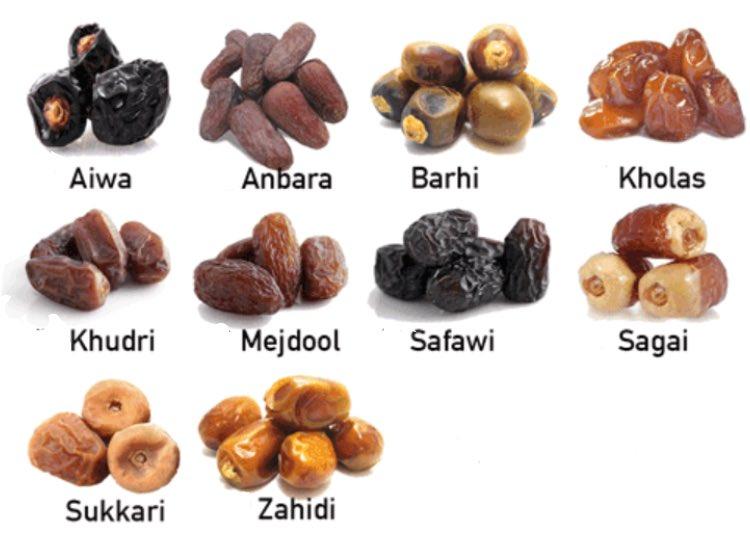

Date Fruits Dataset of 10 classes
Please contact to get the dataset: glatif@pmu.edu.sa
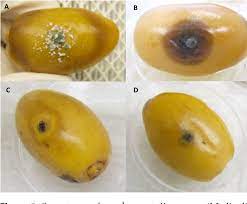
Date Fruit Diseases Dataset of 4 classes
Please contact to get the dataset: glatif@pmu.edu.sa
Supervision (Graduate and Undergraduate Students)
- Shurouq Alufaisan
- Wafa Albur
- Shaikha Alsedrah
- Shahad Alghamdi
- Mariam Alabkari
- Fatima Aljishi
- Shurouq Alufaisan
- Wafa Albur
- Intessar Nasser A Alawadh
- Shaikha Alsedrah
- Ayyah Abdulhafith Mahmoud
- Danyah A Alghmgham
- Roaa AlKhalaf
- Rawan AlKhalaf
- Kinza Waqar
- Shifa Khaja
- Sarah Khan
- Batool Alsalem
- Iman Mohiuddin
- Iman Mohiuddin
- Eman Shaikh
- Ayisha Manzoor
